AFFECT FLOW
AFFECT FLOW (2022)
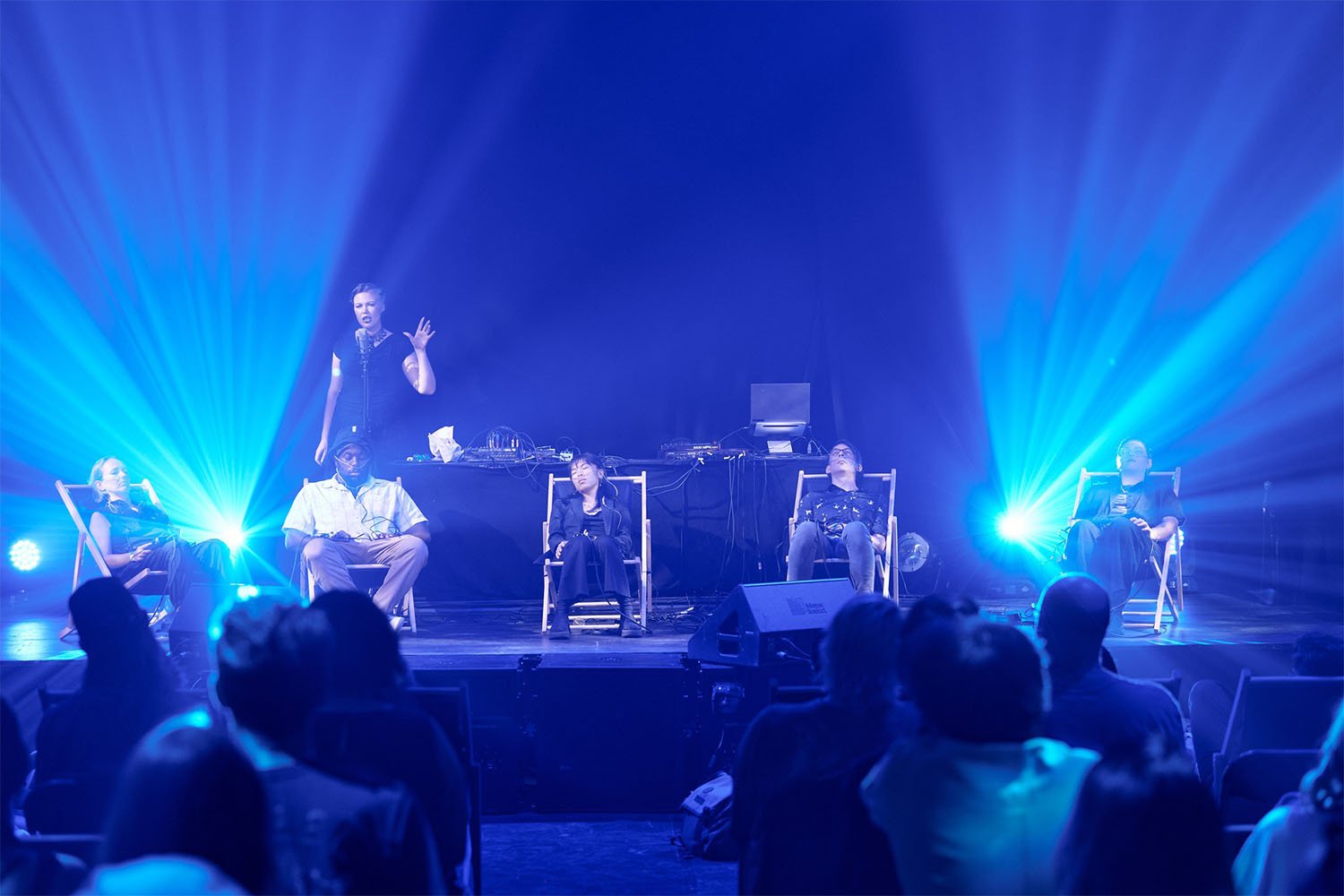
Performance at MUTEK Montreal 2023. Photography by Vivien Gaumand.
2022
AFFECT FLOW is a music performance work of approximately 30 minutes that initiates listeners into a state of “non-naturalist emotion”: emotional manufacture as a technology for survival or pleasure. It is a hybrid of electroacoustic music with live-spoken verbal suggestion, an ensemble of live biofeedback created by hardware synthesisers, and song.
In AFFECT FLOW I use psychological hacks borrowed from method acting and clinical psychology in order to move beyond “natural” emotion, playing with biofeedback music paradigms and group participation through folk hypnosis, verbal suggestion, clinical psychology methods, roleplay, song, and textural sounds.
These performance techniques, which I call “wetware,” challenge the authoritarian aura of quantification, transforming biofeedback into a feminist space of posthumanist connection and expression.
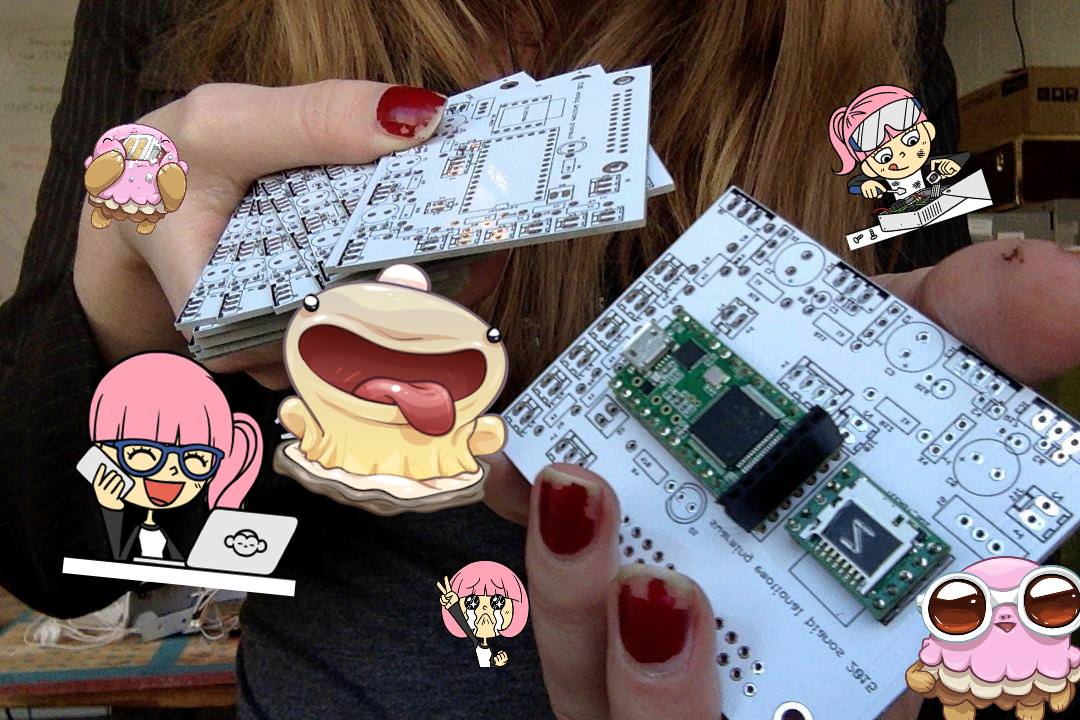
The biofeedback performers (up to 10) in AFFECT FLOW are volunteers referred to as surrogates who meet me a half hour before the performance. After a brief musical interlude, I extend an invitation for the audience to join us in guided visualization and hypnosis led by me and my voice. Each surrogate operates a BioSynth, a musical instrument of my design that responds to physiological markers like heart rate, breathing, and skin conductance as a control parameter for electronic sound. The mechanics of the BioSynths are explained clearly, allowing listeners to perceive the shifting mood in the room during the performance through the bodies of the performers. This collaborative interplay of bodies gives rise to affect as an ecological relation, transcending individual subjectivity.
A lightbulb illuminates at the feet of each performer when their signals are amplified. Because I can control the audio outputs of each body via a mixing board, I can highlight solos, duets, trios, and ensemble moments live in the moment.
Credits
Affect Flow (2022)
Music composition and performance by Erin Gee.
Dramaturgy and text by Jena McLean. Poetry by Andrew C. Wenaus.
BioSynth affective hardware synthesizers are an open-source project by Erin Gee. Programming for this iteration by Etienne Montenegro with sonification programming by Erin Gee. PCB design by Grégory Perrin.
Performances:
International Symposium of Electronic Art. CCCB Barcelona, ES, May 2022.
Society for Art and Technology, Montreal CA, July 2022.
Vancouver New Music – Orpheum Annex, Vancouver CA November 2022.
Electric Eclectics Festival, Meaford ON, CA, August 2023
MUTEK Montreal, CA, August 2023.